使用 Firestore 新增多人連線支援
多人連線遊戲需要一種方式來同步玩家之間的遊戲狀態。 大致上,多人連線遊戲可分為兩種類型:
高 tick 率。 這類遊戲需要每秒多次、低延遲地同步遊戲狀態。 包括動作遊戲、運動遊戲、格鬥遊戲等。
低 tick 率。 這類遊戲只需偶爾同步遊戲狀態,延遲影響較小。 包括紙牌遊戲、策略遊戲、益智遊戲等。
這有點類似於即時遊戲與回合制遊戲的區分,雖然這個比喻並不完全貼切。 例如,即時戰略遊戲(real-time strategy games)顧名思義是在即時運作, 但這並不代表它們需要高 tick 率。 這類遊戲可以在本地端模擬玩家互動之間發生的大部分事件, 因此不需要頻繁地同步遊戲狀態。
如果你作為開發者可以選擇低 tick 率,建議優先選擇。 低 tick 率可降低延遲需求與伺服器成本。 有時候,遊戲確實需要高 tick 率的同步。 在這種情況下,像 Firestore 這樣的解決方案並不適合。 請選擇專用的多人連線伺服器解決方案,例如 Nakama。 Nakama 有提供 Dart 套件。
如果你預期你的遊戲只需要低 tick 率的同步, 請繼續閱讀下方內容。
本教學將示範如何使用 cloud_firestore 套件 在你的遊戲中實作多人連線功能。 本教學不需要伺服器, 而是透過兩個或多個客戶端利用 Cloud Firestore 共享遊戲狀態。
1. 為你的遊戲準備多人連線
#撰寫你的遊戲程式碼時,需允許遊戲狀態能夠因應本地事件與遠端事件而改變。 本地事件可以是玩家操作或某些遊戲邏輯; 遠端事件則可能是來自伺服器的世界更新。
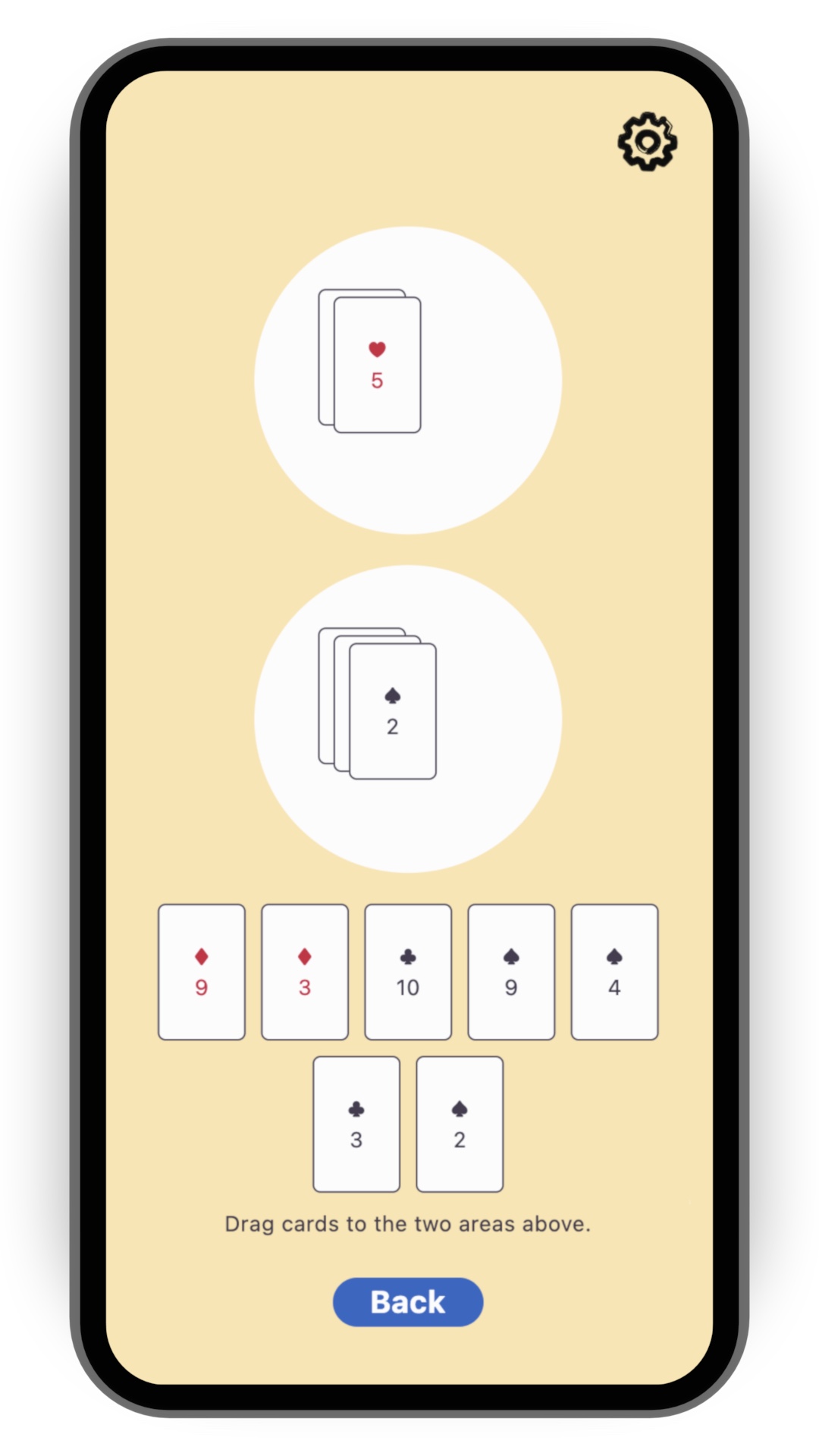
為了簡化本教學,請先從 card 範本開始,你可以在 flutter/games repository 找到該範本。 執行以下指令來複製該 repository:
git clone https://github.com/flutter/games.git在 templates/card 中開啟專案。
2. 安裝 Firestore
#Cloud Firestore 是一個可橫向擴展的雲端 NoSQL 文件資料庫, 並內建即時同步功能。 這非常適合我們的需求。 它能讓遊戲狀態即時同步到雲端資料庫, 確保每位玩家都能看到相同的狀態。
如果你想快速了解 Cloud Firestore,可以參考以下 15 分鐘的入門影片:
Watch on YouTube in a new tab: "What is a NoSQL Database? Learn about Cloud Firestore"
要將 Firestore 加入你的 Flutter 專案, 請依照Cloud Firestore 入門指南的前兩個步驟操作:
完成後,你應該會有以下成果:
- 一個已在雲端啟用、測試模式的 Firestore 資料庫
- 一個已產生的
firebase_options.dart檔案 - 已將相關套件加入你的
pubspec.yaml
這個步驟不需要撰寫任何 Dart 程式碼。 當你閱讀到該指南中需要撰寫 Dart 程式碼的步驟時,請回到本教學食譜繼續操作。
3. 初始化 Firestore
#開啟
lib/main.dart,並匯入相關套件, 以及在前一個步驟由flutterfire configure產生的firebase_options.dart檔案。dartimport 'package:cloud_firestore/cloud_firestore.dart'; import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart'; import 'firebase_options.dart';在
lib/main.dart中呼叫runApp()之前,請在其上方加入以下程式碼:dartWidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized(); await Firebase.initializeApp(options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform);這可確保在遊戲啟動時初始化 Firebase。
將 Firestore 實例加入應用程式。 這樣,任何元件(Widget)都能存取這個實例。 如果需要,元件也可以對實例不存在的情況做出反應。
若要在
card樣板中實現這個功能,你可以使用provider套件 (這個套件已經作為相依套件安裝好)。請將樣板中的
runApp(MyApp())替換為以下內容:dartrunApp(Provider.value(value: FirebaseFirestore.instance, child: MyApp()));請將 provider 放在
MyApp的外層,而不是放在其內部。
這樣可以讓你在沒有 Firebase 的情況下測試應用程式。
4. 建立 Firestore 控制器類別
#雖然你可以直接與 Firestore 溝通,
但建議你撰寫專屬的控制器類別,
讓程式碼更易讀且更容易維護。
控制器的實作方式會依你的遊戲
以及多人遊戲體驗的設計細節而有所不同。
以 card 範本為例,
你可以同步兩個圓形遊戲區域的內容。
雖然這還不足以實現完整的多人遊戲體驗,
但已經是一個很好的起點。
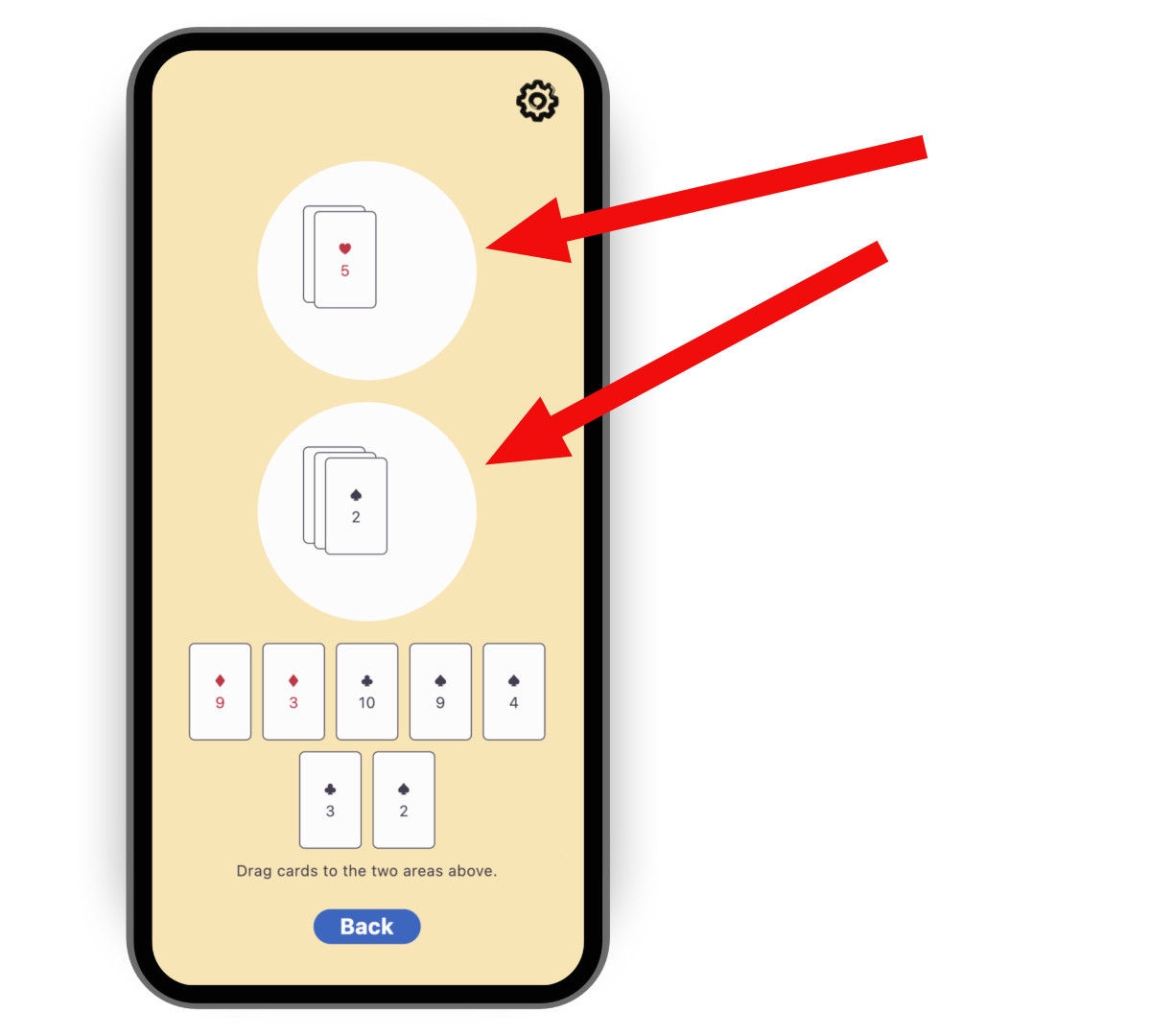
要建立控制器,請複製下方程式碼,
然後貼到一個名為
lib/multiplayer/firestore_controller.dart 的新檔案中。
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:cloud_firestore/cloud_firestore.dart';
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
import 'package:logging/logging.dart';
import '../game_internals/board_state.dart';
import '../game_internals/playing_area.dart';
import '../game_internals/playing_card.dart';
class FirestoreController {
static final _log = Logger('FirestoreController');
final FirebaseFirestore instance;
final BoardState boardState;
/// For now, there is only one match. But in order to be ready
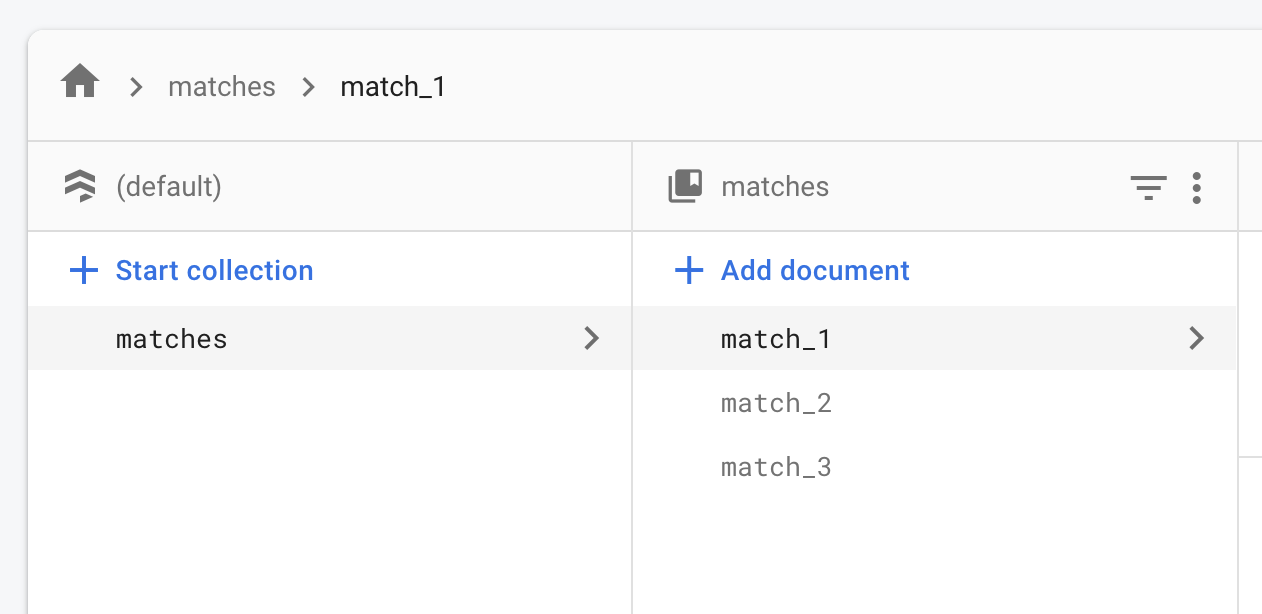
/// for match-making, put it in a Firestore collection called matches.
late final _matchRef = instance.collection('matches').doc('match_1');
late final _areaOneRef = _matchRef
.collection('areas')
.doc('area_one')
.withConverter<List<PlayingCard>>(
fromFirestore: _cardsFromFirestore,
toFirestore: _cardsToFirestore,
);
late final _areaTwoRef = _matchRef
.collection('areas')
.doc('area_two')
.withConverter<List<PlayingCard>>(
fromFirestore: _cardsFromFirestore,
toFirestore: _cardsToFirestore,
);
late final StreamSubscription<void> _areaOneFirestoreSubscription;
late final StreamSubscription<void> _areaTwoFirestoreSubscription;
late final StreamSubscription<void> _areaOneLocalSubscription;
late final StreamSubscription<void> _areaTwoLocalSubscription;
FirestoreController({required this.instance, required this.boardState}) {
// Subscribe to the remote changes (from Firestore).
_areaOneFirestoreSubscription = _areaOneRef.snapshots().listen((snapshot) {
_updateLocalFromFirestore(boardState.areaOne, snapshot);
});
_areaTwoFirestoreSubscription = _areaTwoRef.snapshots().listen((snapshot) {
_updateLocalFromFirestore(boardState.areaTwo, snapshot);
});
// Subscribe to the local changes in game state.
_areaOneLocalSubscription = boardState.areaOne.playerChanges.listen((_) {
_updateFirestoreFromLocalAreaOne();
});
_areaTwoLocalSubscription = boardState.areaTwo.playerChanges.listen((_) {
_updateFirestoreFromLocalAreaTwo();
});
_log.fine('Initialized');
}
void dispose() {
_areaOneFirestoreSubscription.cancel();
_areaTwoFirestoreSubscription.cancel();
_areaOneLocalSubscription.cancel();
_areaTwoLocalSubscription.cancel();
_log.fine('Disposed');
}
/// Takes the raw JSON snapshot coming from Firestore and attempts to
/// convert it into a list of [PlayingCard]s.
List<PlayingCard> _cardsFromFirestore(
DocumentSnapshot<Map<String, Object?>> snapshot,
SnapshotOptions? options,
) {
final data = snapshot.data()?['cards'] as List<Object?>?;
if (data == null) {
_log.info('No data found on Firestore, returning empty list');
return [];
}
try {
return data
.cast<Map<String, Object?>>()
.map(PlayingCard.fromJson)
.toList();
} catch (e) {
throw FirebaseControllerException(
'Failed to parse data from Firestore: $e',
);
}
}
/// Takes a list of [PlayingCard]s and converts it into a JSON object
/// that can be saved into Firestore.
Map<String, Object?> _cardsToFirestore(
List<PlayingCard> cards,
SetOptions? options,
) {
return {'cards': cards.map((c) => c.toJson()).toList()};
}
/// Updates Firestore with the local state of [area].
Future<void> _updateFirestoreFromLocal(
PlayingArea area,
DocumentReference<List<PlayingCard>> ref,
) async {
try {
_log.fine('Updating Firestore with local data (${area.cards}) ...');
await ref.set(area.cards);
_log.fine('... done updating.');
} catch (e) {
throw FirebaseControllerException(
'Failed to update Firestore with local data (${area.cards}): $e',
);
}
}
/// Sends the local state of `boardState.areaOne` to Firestore.
void _updateFirestoreFromLocalAreaOne() {
_updateFirestoreFromLocal(boardState.areaOne, _areaOneRef);
}
/// Sends the local state of `boardState.areaTwo` to Firestore.
void _updateFirestoreFromLocalAreaTwo() {
_updateFirestoreFromLocal(boardState.areaTwo, _areaTwoRef);
}
/// Updates the local state of [area] with the data from Firestore.
void _updateLocalFromFirestore(
PlayingArea area,
DocumentSnapshot<List<PlayingCard>> snapshot,
) {
_log.fine('Received new data from Firestore (${snapshot.data()})');
final cards = snapshot.data() ?? [];
if (listEquals(cards, area.cards)) {
_log.fine('No change');
} else {
_log.fine('Updating local data with Firestore data ($cards)');
area.replaceWith(cards);
}
}
}
class FirebaseControllerException implements Exception {
final String message;
FirebaseControllerException(this.message);
@override
String toString() => 'FirebaseControllerException: $message';
}請注意下列這段程式碼的特點:
控制器的建構子會接收
BoardState。 這讓控制器能夠操作遊戲的本地狀態。控制器同時訂閱本地變更(以更新 Firestore)以及遠端變更(以更新本地狀態與 UI)。
欄位
_areaOneRef和_areaTwoRef是 Firebase 文件參照(document references)。 它們描述了每個區域的資料儲存位置, 以及如何在本地 Dart 物件(List<PlayingCard>) 和遠端 JSON 物件(Map<String, dynamic>)之間進行轉換。 Firestore API 允許我們透過.snapshots()訂閱這些參照, 並用.set()寫入資料。
5. 使用 Firestore 控制器
#開啟負責啟動遊戲對戰(play session)的檔案: 以
card範本為例,為lib/play_session/play_session_screen.dart。 你會在這個檔案中實例化 Firestore 控制器。匯入 Firebase 以及控制器:
dartimport 'package:cloud_firestore/cloud_firestore.dart'; import '../multiplayer/firestore_controller.dart';在
_PlaySessionScreenState類別中新增一個可為 null 的欄位, 用來儲存 controller 實例:dartFirestoreController? _firestoreController;在同一個類別的
initState()方法中, 新增程式碼以嘗試讀取 FirebaseFirestore 實例, 並在成功時建立控制器。 你已經在 初始化 Firestore 步驟中, 將FirebaseFirestore實例加入到main.dart。dartfinal firestore = context.read<FirebaseFirestore?>(); if (firestore == null) { _log.warning( "Firestore instance wasn't provided. " 'Running without _firestoreController.', ); } else { _firestoreController = FirestoreController( instance: firestore, boardState: _boardState, ); }使用同一個類別的
dispose()方法來釋放 controller。dart_firestoreController?.dispose();
6. 測試遊戲
#在兩個不同的裝置上運行遊戲, 或在同一裝置的兩個不同視窗中運行。
觀察在一個裝置上將卡牌加入某個區域時, 另一個裝置也會即時顯示該卡牌。
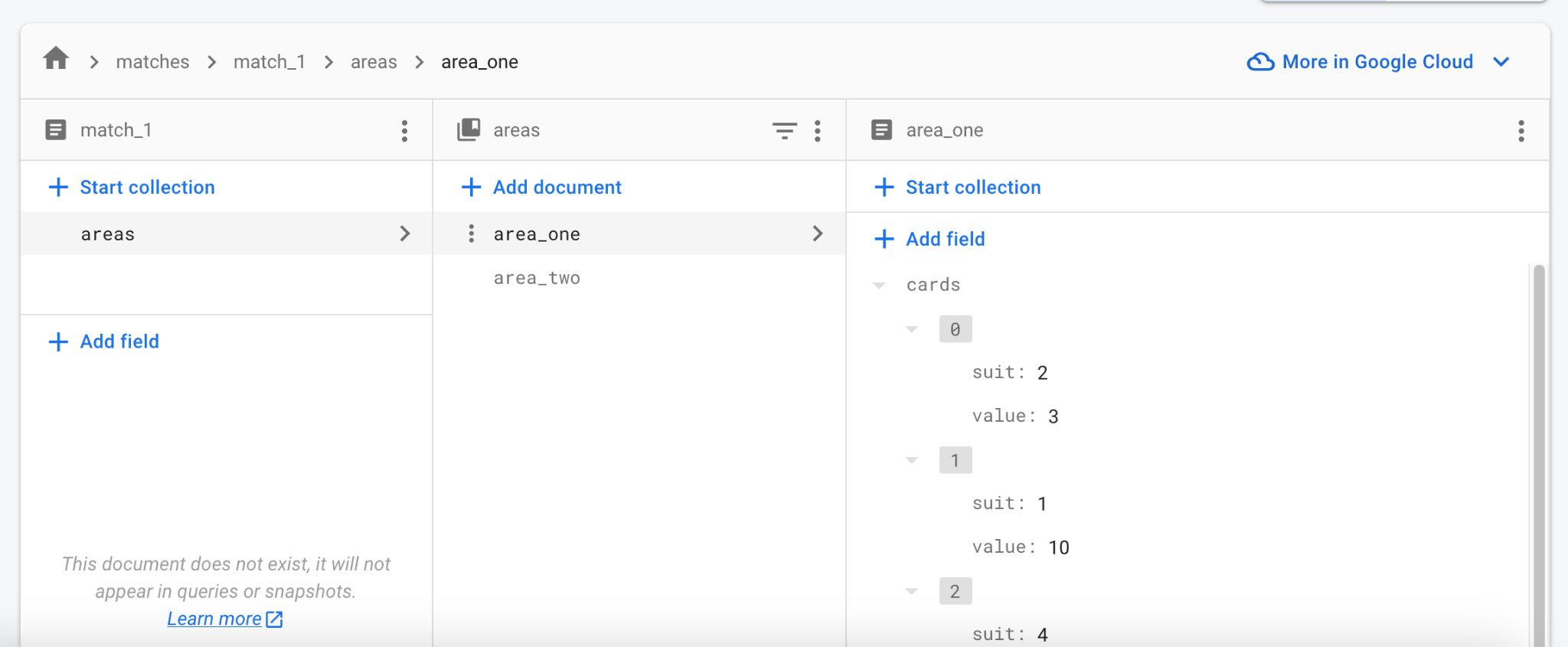
開啟 Firebase 網頁主控台, 並導覽至你的專案的 Firestore Database。
觀察資料如何即時更新。 你甚至可以在主控台直接編輯資料, 所有正在運行的客戶端都會同步更新。
疑難排解
#測試 Firebase 整合時,最常見的問題包括:
遊戲在嘗試連接 Firebase 時當機。
- Firebase 整合尚未正確設定。 請回到 步驟 2,並確保有執行
flutterfire configure作為該步驟的一部分。
- Firebase 整合尚未正確設定。 請回到 步驟 2,並確保有執行
遊戲在 macOS 上無法與 Firebase 通訊。
- macOS 應用程式預設無法存取網際網路。 請先啟用 網路權限 (internet entitlement)。
7. 下一步
#此時,遊戲已能在多個客戶端之間 實現近乎即時且可靠的狀態同步。 但目前還沒有實際的遊戲規則: 例如什麼時候可以出什麼卡牌,以及會有什麼結果。 這部分取決於你設計的遊戲,留給你自行嘗試。

目前,對戰的共享狀態僅包含 兩個遊戲區域及其內的卡牌。 你也可以將其他資料存入 _matchRef, 例如玩家是誰、輪到誰出牌等。 如果你不確定從哪裡開始, 可以參考 一兩個 Firestore codelab 來熟悉這個 API。
一開始,單一場對戰就足以 讓你和同事、朋友測試多人遊戲功能。 當你接近發佈時, 可以開始考慮身份驗證和配對機制。 幸運的是,Firebase 提供了 內建的使用者驗證方式, 而 Firestore 的資料結構也能支援多場對戰。 你可以將多筆紀錄加入 matches collection, 而不是只用單一 match_1。
一場線上對戰可以從「等待中」狀態開始, 此時只有第一位玩家在場。 其他玩家可以在大廳看到「等待中」的對戰。 當有足夠玩家加入後,對戰就會變成「進行中」。 具體的實作方式仍取決於 你想要打造的線上體驗類型。 但基本原則相同: 有一個大型的文件集合, 每一份文件都代表一場進行中或潛在的對戰。