各層之間的溝通
除了為架構中的每個元件(Component)定義明確的職責之外, 同時也必須考慮這些元件之間如何溝通。 這不僅包括規範元件之間溝通的規則, 也涵蓋了元件之間實際溝通的技術實作方式。 一個應用程式的架構應該能夠回答以下問題:
- 哪些元件允許與哪些其他元件溝通 (包含相同型別的元件)?
- 這些元件彼此之間會暴露哪些輸出?
- 各層之間是如何「串接」在一起的?
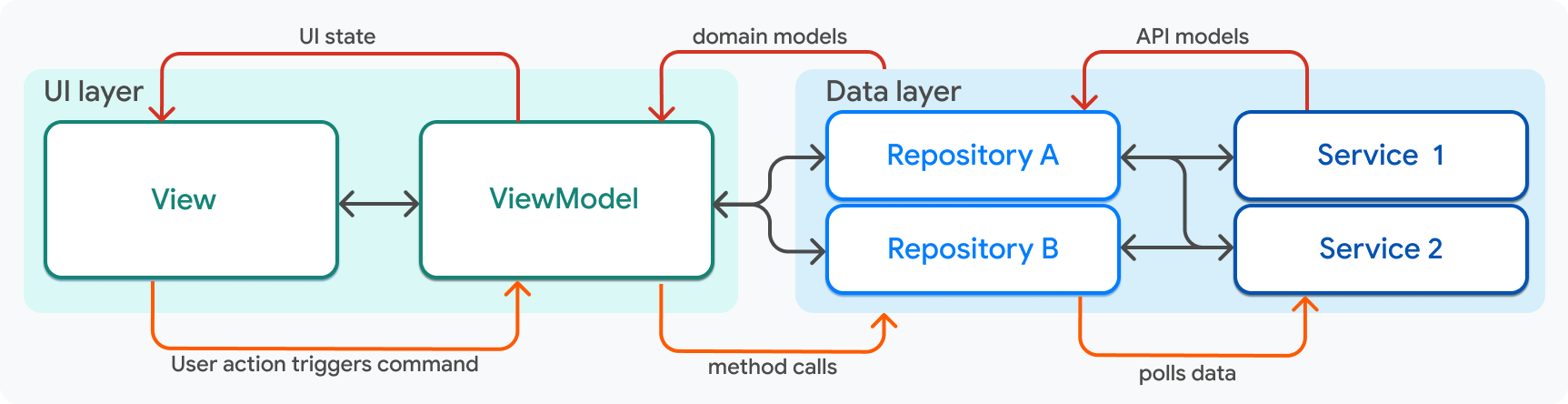
以此圖為指引,溝通規則如下:
| 元件 | 溝通規則 |
|---|---|
| View |
|
| ViewModel |
|
| Repository |
|
| Service |
|
依賴注入(Dependency injection)
#本指南已展示這些不同元件如何透過輸入與輸出彼此溝通。 在每一種情境下,兩層之間的溝通都是透過將一個元件 作為參數傳入建構子(由需要消費其資料的元件), 例如將 Service 傳入 Repository.
class MyRepository {
MyRepository({required MyService myService})
: _myService = myService;
late final MyService _myService;
}然而,目前還缺少一個重要的部分:物件的建立。在應用程式中,MyService 實例究竟是在何處被建立,才能傳遞給 MyRepository 呢? 這個問題的答案涉及一種稱為 依賴注入(dependency injection) 的設計模式。
在 Compass 應用程式中,依賴注入(dependency injection) 是透過 package:provider 來處理的。根據 Google 團隊在建構 Flutter 應用程式的經驗,建議使用 package:provider 來實作依賴注入。
服務(services)和資料儲存庫(repositories)會以 Provider 物件的形式,暴露在 Flutter 應用程式元件樹(widget tree)的最上層。
runApp(
MultiProvider(
providers: [
Provider(create: (context) => AuthApiClient()),
Provider(create: (context) => ApiClient()),
Provider(create: (context) => SharedPreferencesService()),
ChangeNotifierProvider(
create: (context) => AuthRepositoryRemote(
authApiClient: context.read(),
apiClient: context.read(),
sharedPreferencesService: context.read(),
) as AuthRepository,
),
Provider(create: (context) =>
DestinationRepositoryRemote(
apiClient: context.read(),
) as DestinationRepository,
),
Provider(create: (context) =>
ContinentRepositoryRemote(
apiClient: context.read(),
) as ContinentRepository,
),
// In the Compass app, additional service and repository providers live here.
],
child: const MainApp(),
),
);Services 之所以被公開,是為了能夠立即透過 provider 的 BuildContext.read 方法注入到 repositories 中,如前述程式碼片段所示。
接著,repositories 會被公開,以便在需要時注入到 view models 中。
在 widget tree 稍微下層的位置,對應整個螢幕的 view models 會在 package:go_router 設定中建立,此時同樣使用 provider 來注入所需的 repositories。
// This code was modified for demo purposes.
GoRouter router(
AuthRepository authRepository,
) =>
GoRouter(
initialLocation: Routes.home,
debugLogDiagnostics: true,
redirect: _redirect,
refreshListenable: authRepository,
routes: [
GoRoute(
path: Routes.login,
builder: (context, state) {
return LoginScreen(
viewModel: LoginViewModel(
authRepository: context.read(),
),
);
},
),
GoRoute(
path: Routes.home,
builder: (context, state) {
final viewModel = HomeViewModel(
bookingRepository: context.read(),
);
return HomeScreen(viewModel: viewModel);
},
routes: [
// ...
],
),
],
);在 view model 或 repository 中,被注入的元件應該設為 private(私有)。 例如,HomeViewModel 類別會像這樣:
class HomeViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
HomeViewModel({
required BookingRepository bookingRepository,
required UserRepository userRepository,
}) : _bookingRepository = bookingRepository,
_userRepository = userRepository;
final BookingRepository _bookingRepository;
final UserRepository _userRepository;
// ...
}私有方法可防止具有 view model 存取權限的 view,直接呼叫 repository 上的方法。
以上就是 Compass 應用程式的程式碼導覽。本頁僅介紹了與架構相關的程式碼,並未涵蓋全部內容。大多數工具程式碼、元件(Widgets)程式碼,以及 UI 樣式設定都未提及。請瀏覽 Compass app repository,以取得依循這些原則所打造的完整且健全的 Flutter 應用程式範例。
意見回饋
#由於本網站的這個章節仍在持續演進中, 我們歡迎您的意見回饋!